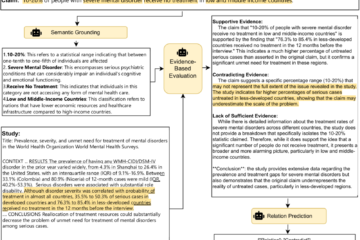
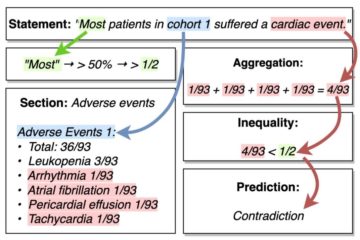
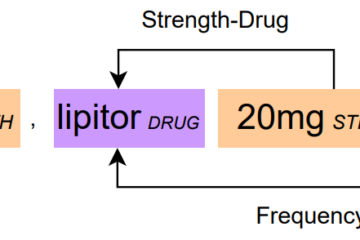
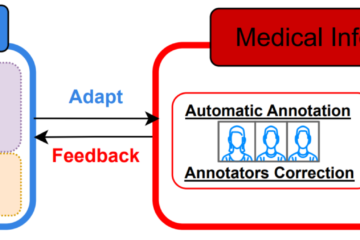
Explainable Biomedical Claim Verification (Accenture)
In the Autoprompt project funded by a grant from Accenture, one of the world’s leading consulting, technology and outsourcing companies, we focus on developing automated biomedical claim verification systems designed to assist clinicians and researchers in addressing the risks posed by misinformation in the healthcare domain. By providing accurate, evidence-based Read more