Starting from its inception in 1969, the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) has been the premier venue for the global AI community to share and celebrate advancements in artificial intelligence research. This year’s edition took place in Jeju, South Korea (main conference acceptance rate 15%), and the Interactive Machine Learning (IML) group presented two studies demonstrating the power of interactive systems that leverage pre-trained machine learning models. Focused on different application areas—wildlife monitoring and journalism—these studies share a common goal: improving the efficiency and effectiveness of critical tasks through the integration of advanced machine learning techniques with human expertise.
At the main conference’s demo track, our team introduced an innovative no-code annotation tool designed to streamline the analysis of Passive Acoustic Monitoring (PAM) datasets, which are crucial for wildlife monitoring. PAM generates extensive acoustic data, necessitating efficient annotation for accurate sound event detection. Our tool integrates transfer learning and active learning strategies to optimize this process. By utilizing pre-trained models to derive meaningful audio embeddings and an active learning approach to identify the most informative samples, the tool significantly accelerates the annotation process—improving efficiency by 2-4 times compared to traditional methods. This advancement has the potential to greatly benefit research and conservation efforts by making large-scale data annotation more accessible and efficient.
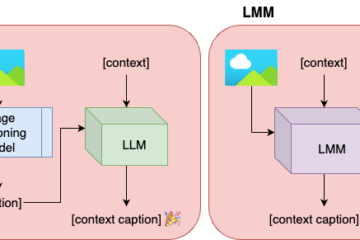
Additionally, at the Trustworthy Interactive Decision Making with Foundation Models workshop, our researchers presented a study exploring the role of AI in journalism. This research focused on how large language and multimodal models can generate contextualized captions for news images, demonstrating AI’s potential to enhance the quality and efficiency of news reporting. The study also emphasized the critical role of human involvement to ensure optimal outcomes. These findings extend beyond journalism, offering insights that could impact fields like content creation, digital marketing, and education, where AI combined with human expertise can improve the accuracy and reliability of automated outputs.

IJCAI conference on Jeju Island, South Korea (Photo: Reproduction from social media)
References
Kath, H., Serafini, P. P., Campos, I. B., Gouvêa, T. S., & Sonntag, D. (2024). Demo: Enhancing Wildlife Acoustic Data Annotation Efficiency through Transfer and Active Learning. Proceedings of the 33rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 8691–8695. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2024/1010
Anagnostopoulou, A., Gouvêa, T. S., & Sonntag, D. (2024). Enhancing Journalism with AI: A Study of Contextualized Image Captioning for News Articles using LLMs and LMMs. Trustworthy Interactive Decision Making with Foundation Models workshop, 33rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.04331