IML was represented with two full papers and a short paper at this year’s KI conference in Berlin.
“Lost in Dialogue: A Review and Categorisation of Current Dialogue System Approaches and Technical Solutions” by Hannes Kath, Bengt Lüers, Thiago S. Gouvêa, and Daniel Sonntag provides a categorisation of dialogue systems according to the objective, modality, domain, architecture, and model, and provides information on the correlations among these categories. The authors summarise and compare frameworks and applications of intelligent virtual assistants, commercial frameworks, research dialogue systems, and large language models according to these categories and provide system recommendations for researchers new to the field.
In “Interactive Link Prediction as a Downstream Task for Foundational GUI Understanding Models“, Christoph Albert Johns, Michael Barz, and Daniel Sonntag present interactive link prediction as a downstream task for GUI understanding models and provide baselines as well as testing tools to effectively and efficiently evaluate predictive GUI understanding models.
“Harmonizing Feature Attributions Across Deep Learning Architectures: Enhancing Interpretability and Consistency” by Md Abdul Kadir, Gowthamkrishna Addluri, and Daniel Sonntag delves into the learning patterns of different neural architectures from the same data distribution and how these learned features correlate with each other. The study scrutinizes the generalization of feature attributions across a variety of deep learning architectures, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers.
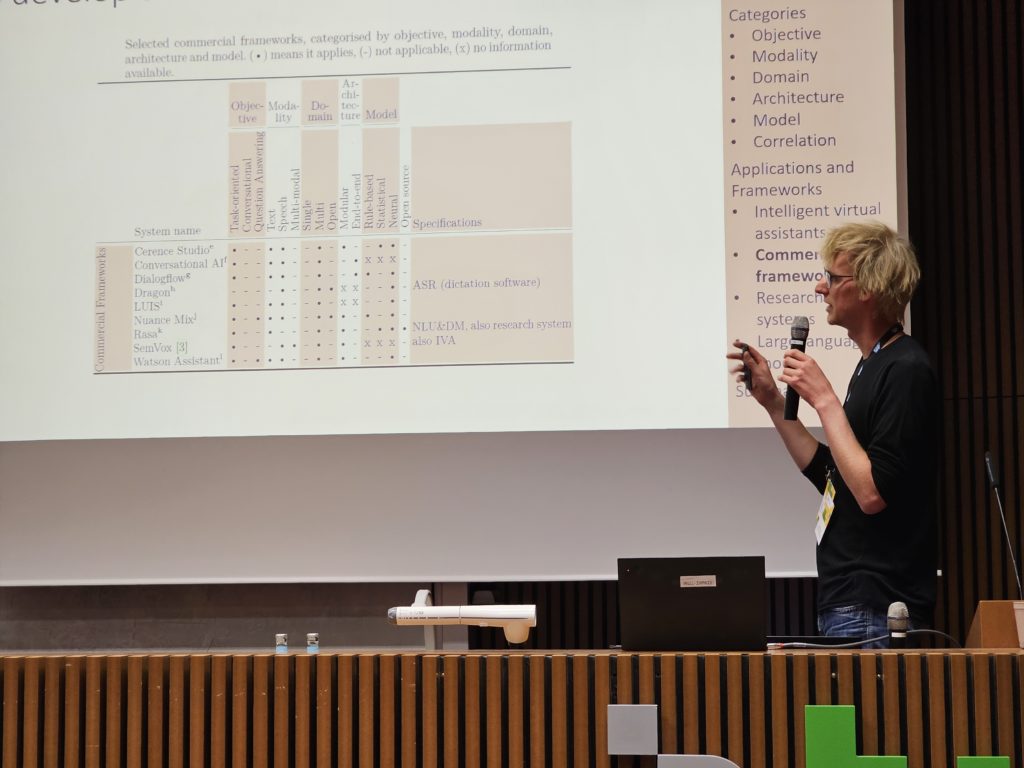

Hannes Kath from IML presents the paper “Lost in Dialogue: A Review and Categorisation of Current Dialogue System Approaches and Technical Solutions” in Berlin

Michael Barz from IML presents the paper “Interactive Link Prediction as a Downstream Task for Foundational GUI Understanding Models”