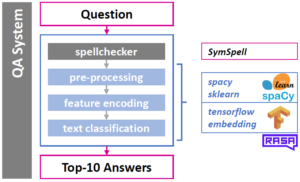
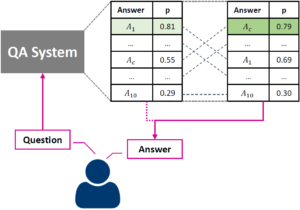
We implement a method for re-ranking top-10 results of a state-of-the-art question answering (QA) system. The goal of our re-ranking approach is to improve the answer selection given the user question and the top-10 candidates. We focus on improving deployed QA systems that do not allow re-training or when re-training comes at a high cost. Our re-ranking approach learns a similarity function using n-gram based features using the query, the answer and the initial system confidence as input. Our contributions are: (1) we generate a QA training corpus starting from 877 answers from the customer care domain of T-Mobile Austria, (2) we implement a state-of-the-art QA pipeline using neural sentence embeddings that encode queries in the same space than the answer index, and (3) we evaluate the QA pipeline and our re-ranking approach using a separately provided test set. The test set can be considered to be available after deployment of the system, e.g., based on feedback of users. Our results show that the system performance, in terms of top-n accuracy and the mean reciprocal rank, benefits from re-ranking using gradient boosted regression trees. On average, the mean reciprocal rank improves by 9.15%.
References
- Incremental Improvement of a Question Answering System by Re-ranking Answer Candidates using Machine Learning. In: Computing Research Repository eprint Journal, abs/1908.10149 , pp. 1-13, 2019.
Supported by